The Differential Global Positioning System: A Complete Overview
Introduction to DGPS
The Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) is an advanced enhancement to the standard Global Positioning System (GPS), providing significantly improved location accuracy. While conventional GPS can have errors ranging from a few meters to several meters, DGPS refines positional data to an accuracy of up to 10 cm or better. This enhanced precision is crucial for various sectors, including land surveying, marine navigation, construction, and geospatial applications.
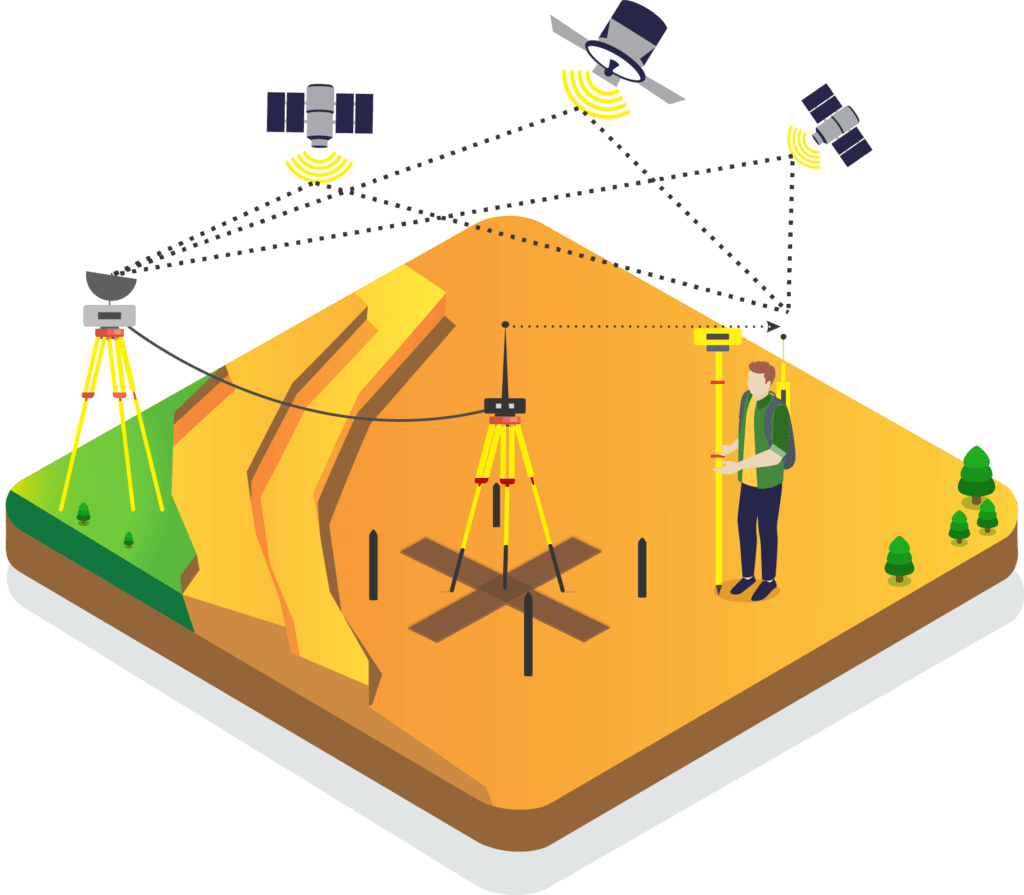
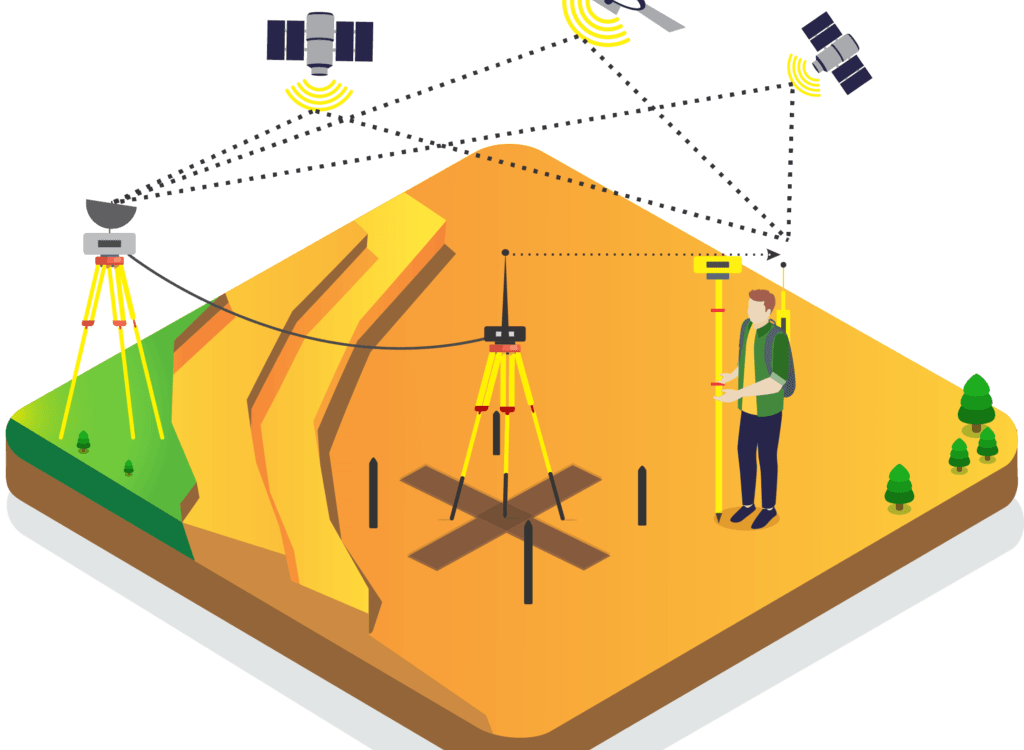
How DGPS Works
DGPS works by using a network of fixed ground-based reference stations that calculate and transmit error corrections to GPS receivers. These corrections eliminate inaccuracies caused by satellite orbit errors, atmospheric conditions, and timing errors. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Reference Station Monitoring – A stationary reference station at a known fixed location receives GPS signals and determines the difference between the actual and observed position.
- Error Calculation – The reference station computes the necessary corrections based on signal discrepancies.
- Correction Transmission – The error corrections are then transmitted via radio signals or internet-based services to nearby DGPS-enabled receivers.
- Enhanced Positioning – The DGPS receivers apply the corrections, resulting in highly accurate positioning data.
Advantages of DGPS
- Enhanced Accuracy: Reduces positional errors significantly, improving navigation and mapping precision.
- Reliable Performance: Works effectively in challenging environments such as urban landscapes and coastal regions.
- Improved Safety: Ensures precise positioning for critical applications like aviation, maritime navigation, and autonomous vehicle guidance.
- Efficient Land Surveying: Used by professional land surveyors in Coimbatore and worldwide to generate precise topographic maps and boundary demarcations.
Applications of DGPS
DGPS plays a crucial role in various industries, making it a preferred choice for high-accuracy positioning requirements:
1. Land Surveying and Mapping
Surveyors use DGPS for boundary mapping, topographical surveys, and infrastructure planning. The accuracy provided by DGPS helps in defining property lines and planning large-scale construction projects.
2. Marine and Aviation Navigation
Maritime and aviation industries rely on DGPS for safe navigation, port docking, and flight path monitoring. DGPS significantly reduces navigational errors, preventing accidents and improving efficiency.
3. Agriculture and Precision Farming
DGPS enables precision agriculture by assisting in automated tractor guidance, crop monitoring, and soil analysis. Farmers can optimize field usage, reduce waste, and improve yield quality.
4. Infrastructure and Construction
Construction projects, including roads, bridges, and railways, require highly accurate earthwork and alignment measurements. Land surveyors in Coimbatore use DGPS technology to enhance project planning and execution.
5. Disaster Management and Emergency Services
Emergency response teams utilize DGPS for search and rescue operations, disaster recovery planning, and real-time location tracking to ensure faster and more effective responses.
DGPS vs. GPS: Key Differences
| Feature | GPS | DGPS |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 5-15 meters | Up to 10 cm |
| Error Correction | No correction mechanism | Uses ground-based correction signals |
| Signal Reliability | Affected by atmospheric conditions | More stable due to real-time corrections |
| Cost | More affordable | Requires additional equipment for correction |
Challenges and Limitations of DGPS
Despite its advantages, DGPS does have some challenges:
- Signal Dependency: DGPS requires uninterrupted communication with base stations, making it less effective in remote or obstructed locations.
- Cost of Implementation: Setting up DGPS infrastructure involves additional expenses for receivers and correction signal transmission.
- Limited Coverage: DGPS correction signals have a limited range, requiring multiple reference stations for large-area coverage.
Future of DGPS Technology
With the growing demand for precision in navigation, mapping, and automation, DGPS technology continues to evolve. Future advancements include:
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning – Enhancing real-time positioning analytics.
- Expansion of RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) GPS – Providing even higher accuracy for autonomous systems.
- Increased Satellite Networks – Improved global coverage for more reliable positioning.
Conclusion
DGPS remains an essential tool for industries requiring high-precision geospatial data. From land surveyors in Coimbatore to global infrastructure projects, its impact is significant in modern technology applications. As innovations continue, DGPS will play a vital role in shaping the future of navigation, mapping, and automated positioning systems.